Summary
Japan’s sustainable investment assets have grown by 16.4% CAGR1 over the last five years. The strong commitment from both government and corporates to transition to a low-carbon economy by 2050 will create more opportunities going forward.
1. Is Japan narrowing the gap with its peers on the ESG front?
Japan has long been viewed as an ESG laggard within the OECD, weighed by the “E” and “G” factors. For sure, the country’s climate track record is still far from ideal with its heavy reliance on fossil fuels (mainly coal and natural gas). But change is afoot. A new Green Transformation policy was approved in February 2023 to help Japan meet its net-zero goal by 2050. The policy outlines a 10-year roadmap to transition to clean energy via the usage of nuclear power, renewables, and carbon-pricing mechanisms.
While the medium-term transition targets may not achieve a complete break from the reliance on fossil fuels, renewable energy is expected to become the largest power supply source, comprising 37% of the power mix by 2030, thereby contributing to cutting greenhouse emissions by 46% from 2013 levels. Furthermore, if we add the expected comeback of nuclear energy, more than half of the power supply would be low carbon at competitive costs. We believe this will become a game changer for corporates and consumers, particularly if the “reshoring manufacturing” trend drives both domestic and global companies to expand and rebuild manufacturing bases in Japan.
Fig 1: Japan’s power generation capacity mix
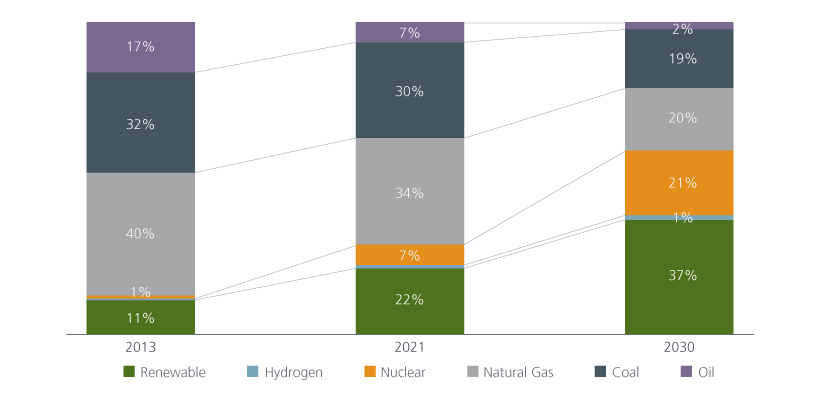
Source: International Energy Agency, Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry, Japan, 2022
The report card on “G” is better with ongoing corporate reforms bearing fruit. The behaviour of Japanese companies has changed significantly. The adoption of best practices, the unravelling of the cross-shareholdings and divestments of non-core businesses have resulted in improved returns on equity. More companies now have independent outside directors and there has been a steady improvement in reducing the number of boards without female representation.
According to the Gender Equality Council under the Cabinet Office, the percentage of the companies with all-male Board of Directors in the Prime segment of Tokyo Stock Exchange was only 18.7% in 2022, a significant decline from 84% in 2013. The government is stepping in to further improve the gender diversity by setting mandatory targets for companies listed in the Prime market; by 2025 all must have a minimum of one female Board member and by 2030 it has to hit 30%.
Fig 2. MSCI company ESG rating concentration across regions
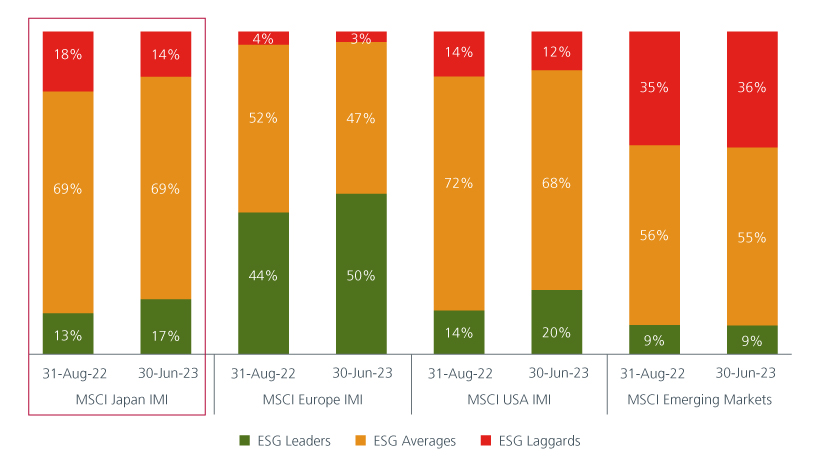
Source: MSCI ESG Research. MSCI IMI are MSCI Investable Market Indexes cover all investable large-, mid- and small-cap securities across markets, targeting approximately 99% of each market’s free-float adjusted market capitalization. MSCI ESG Ratings measure a company's management of financially relevant ESG risks and opportunities. The ESG Ratings range from Leaders (AAA, AA), Averages (A, BBB, BB) to Laggards (B, CCC).
On the “S” pillar, Japanese companies have always done better, having stuck to the unique practice of prioritising the interests of other stakeholders; a centuries old code of ethics (shuchu kiyaku) guides that trade should be mutually beneficial. Japanese companies also have a long tradition of taking care of employees and communities as per the “spirit of the corporation”.
Japan is also the first country to issue a new principles-based code of conduct for ESG ratings and data providers which has been adopted by several major ESG data providers such as FTSE Russell, Moody’s, S&P, Refinitiv and Sustainalytics. This should improve the transparency and quality of ESG ratings and data going forward.
2. Are more Japanese corporates embedding ESG principles?
Japan’s Government Pension Investment Fund (GPIF), the world’s largest pension fund, triggered a chain reaction from 2017 when it began allocating funds to ESG investments. Japanese corporates followed suit by embracing ESG so that their ESG ratings would appeal to GPIF and other investors. More recently, growing investor interest in Japan’s stock market is pressuring listed companies to improve their ESG standards.
We see a lot more companies now disclosing and mapping ESG strategies to the Sustainable Development Goals compared to five years ago. It is worth highlighting that more financial institutions and corporates in Japan support the Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD) than peers. From September 2023, all listed companies will also have to adhere to mandatory disclosure requirements on their sustainability and corporate governance strategies.
Fig 3: Number of institutions supporting the task force on climate-related financial disclosures
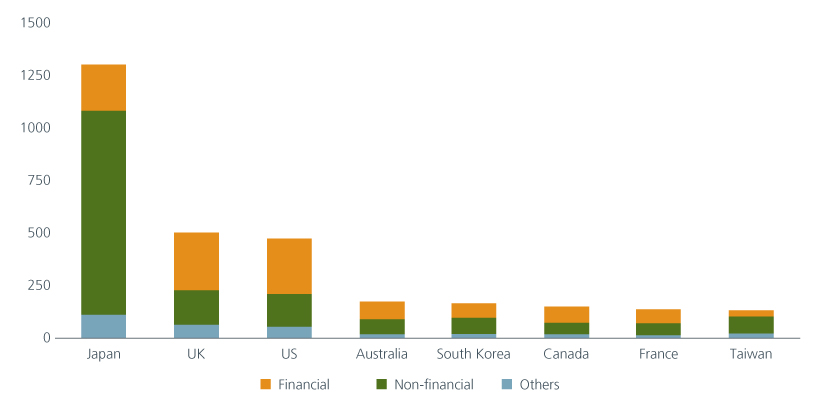
Source: TCFD consortium data as of 24 April 2023
3. What strengths can Japan leverage on to become carbon neutral?
Japan is well known for cutting edge technology. It is thus no surprise that they have a leading inventory of low-carbon technology patents. Japanese companies have a long history of reducing energy consumption and maximising energy efficiency given the scarcity of resources; they have accumulated the largest inventory of battery technologies in the world including lithium-ion batteries (with much higher capacity and durability) and all other solid-state batteries. The challenge is to quickly commercialise these technologies to capture growth opportunities both overseas and locally as Korean and Chinese peers are accelerating their pace of innovation.
The government is also pushing for technological development to take place within a cross-industry framework. By investing in tech innovation, companies can transform their business models and in turn derive business revenues from sustainable solutions.
The other aspect is the drive to become a circular economy. There are strict laws to control waste. Japan’s waste recycling is the highest in the world; plastic recycling for example amounted to 87% in 2021 from 80% in 2012.2
Fig 4: Top low-carbon technology patent holders by countries
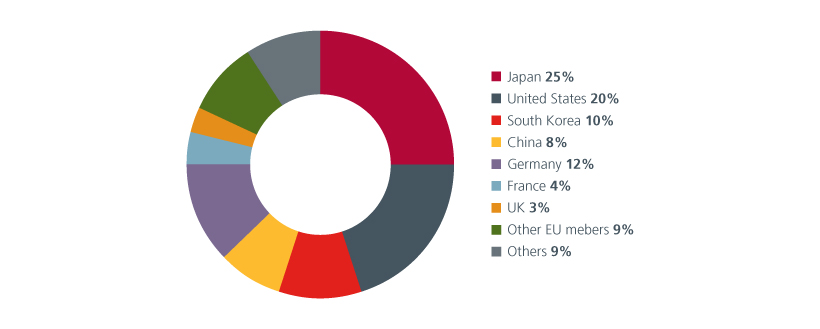
Source: European Patent Office, International Agency, “patents and the energy transition”, April 2023. Data is cumulative (2010-2019)
4. How can asset managers help accelerate Japan’s path to decarbonisation?
Asset managers should continue to encourage companies in their portfolios to address ESG in their business operations. At Eastspring we do this via active engagement and proxy voting, both of which are central to our investment process and stewardship commitment. We will also engage in direct dialogue with the investee company’s management to influence policies on sustainability as well as address and/or rectify the issues as soon as practically possible.
In addition, investee companies are monitored closely if they are on the Watch List for possible violations of Global Norms or assessed as having “Severe and Most Severe Controversies” by third-party research providers. Regular dialogue with senior management and the Board is conducted by our investment team to ensure awareness and willingness to address the issues in a timely manner.
Fig 5: Engagement and shareholder action is Japan’s favoured strategy
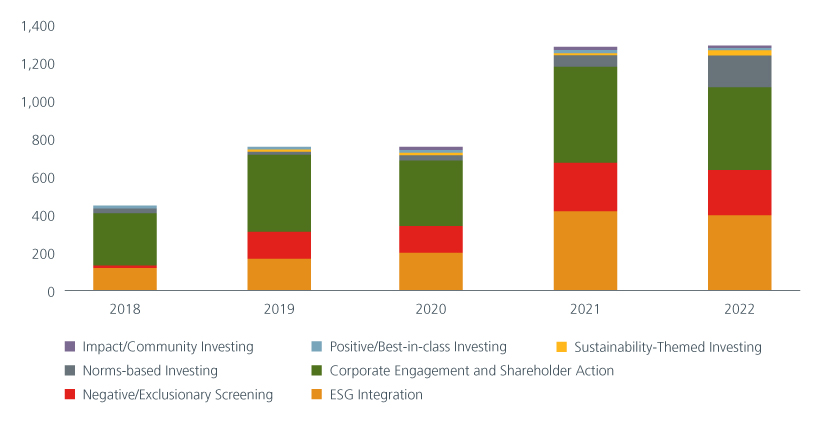
Source: Japan Sustainable Investment Forum (JSIF), April 2023
5. Which sectors offer the most ESG opportunities?
Japan’s green investment opportunities are underappreciated. The sustainable investment universe of listed equities is expanding. Within this space, we observe a diverse range of green business opportunities from activities under research and development such as carbon capture and storage, hydrogen, fuel cells, etc., to activities that are already generating revenues and profits such as electric vehicles, renewable power generation, energy efficiency, pollution prevention, waste treatment and management, water treatment and infrastructure, etc.
Our investment team also considers the EU taxonomy guidelines to identify potential sustainable investment opportunities. This framework helps investors identify and measure business activities that are environmentally sustainable. An analysis of companies with over 5% revenues that are eligible and aligned with the EU Taxonomy in addressing two of the six environmental objectives i.e., climate change mitigation and climate change adaptation, reveal that European and Japanese companies have the highest exposure to sustainable business activities.
Fig 6: Percentage of companies potentially eligible and/or aligned to the EU taxonomy by regions
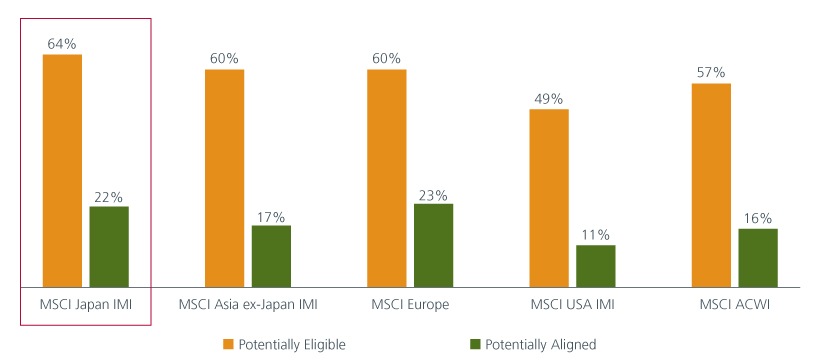
Source: MSCI ESG Research, Eastspring Investments as of 31 March 2023 using 5% revenues as cut off point. MSCI IMI are MSCI Investible Market Indices that cover all investable large-, mid- and small-cap securities across markets, targeting approx. 99% of each market’s free-float adjusted market capitalisation. MSCI ACWI has over 8,000 investable securities.
6. What are some of the biggest challenges for Japan?
On the “E” front, nuclear energy is the way forward, but public sentiment is against it. However geopolitical risks such as the Russia-Ukraine war, Sino-US tension, Middle East uncertainties, etc. may influence Japan’s domestic opinion to favour restarts of idle nuclear power plants. Still significant hurdles remain that prevent the reactivation of these plants.
Japan’s mountainous terrain running through all the four main islands limits the country’s ability to increase its renewable energy sources. According to International Energy Agency, to reach its carbon neutral goal by 2050, Japan would thus need to invest significantly to commercialise low carbon technologies such as hydrogen, fuel cell, carbon capture and storage, etc. alongside existing ones, and infrastructure such as electric vehicles, smart grids, energy storages, robotics, etc.
On corporate governance, remarkable improvement has been achieved in recent years thanks to the efforts of the government, the Financial Services Agency, the Tokyo Stock Exchange, and institutional investors. Despite this, Japan’s current governance practices are still not at par with their US and European peers, especially the Board structures (tenure, diversity, age, quality of directors, etc.).
Sources:
1 Compounded average growth rate from 2018 to 2022 based on data from Japan Sustainable Forum (JSIF) Apr 2023.
2 Statista, 2022.
The information and views expressed herein do not constitute an offer or solicitation to deal in shares of any securities or financial instruments and it is not intended for distribution or use by anyone or entity located in any jurisdiction where such distribution would be unlawful or prohibited. The information does not constitute investment advice or an offer to provide investment advisory or investment management service or the solicitation of an offer to provide investment advisory or investment management services in any jurisdiction in which an offer or solicitation would be unlawful under the securities laws of that jurisdiction.
Past performance and the predictions, projections, or forecasts on the economy, securities markets or the economic trends of the markets are not necessarily indicative of the future or likely performance of Eastspring Investments or any of the strategies managed by Eastspring Investments. An investment is subject to investment risks, including the possible loss of the principal amount invested. Where an investment is denominated in another currency, exchange rates may have an adverse effect on the value price or income of that investment. Furthermore, exposure to a single country market, specific portfolio composition or management techniques may potentially increase volatility.
Any securities mentioned are included for illustration purposes only. It should not be considered a recommendation to purchase or sell such securities. There is no assurance that any security discussed herein will remain in the portfolio at the time you receive this document or that security sold has not been repurchased.
The information provided herein is believed to be reliable at time of publication and based on matters as they exist as of the date of preparation of this report and not as of any future date. Eastspring Investments undertakes no (and disclaims any) obligation to update, modify or amend this document or to otherwise notify you in the event that any matter stated in the materials, or any opinion, projection, forecast or estimate set forth in the document, changes or subsequently becomes inaccurate. Eastspring Investments personnel may develop views and opinions that are not stated in the materials or that are contrary to the views and opinions stated in the materials at any time and from time to time as the result of a negative factor that comes to its attention in respect to an investment or for any other reason or for no reason. Eastspring Investments shall not and shall have no duty to notify you of any such views and opinions. This document is solely for information and does not have any regard to the specific investment objectives, financial or tax situation and the particular needs of any specific person who may receive this document.
Eastspring Investments Inc. (Eastspring US) primary activity is to provide certain marketing, sales servicing, and client support in the US on behalf of Eastspring Investment (Singapore) Limited (“Eastspring Singapore”). Eastspring Singapore is an affiliated investment management entity that is domiciled and registered under, among other regulatory bodies, the Monetary Authority of Singapore (MAS). Eastspring Singapore and Eastspring US are both registered with the US Securities and Exchange Commission as a registered investment adviser. Registration as an adviser does not imply a level of skill or training. Eastspring US seeks to identify and introduce to Eastspring Singapore potential institutional client prospects. Such prospects, once introduced, would contract directly with Eastspring Singapore for any investment management or advisory services. Additional information about Eastspring Singapore and Eastspring US is also is available on the SEC’s website at www.adviserinfo.sec. gov.
Certain information contained herein constitutes "forward-looking statements", which can be identified by the use of forward-looking terminology such as "may", "will", "should", "expect", "anticipate", "project", "estimate", "intend", "continue" or "believe" or the negatives thereof, other variations thereof or comparable terminology. Such information is based on expectations, estimates and projections (and assumptions underlying such information) and cannot be relied upon as a guarantee of future performance. Due to various risks and uncertainties, actual events or results, or the actual performance of any fund may differ materially from those reflected or contemplated in such forward-looking statements.
Eastspring Investments companies (excluding JV companies) are ultimately wholly-owned / indirect subsidiaries / associate of Prudential plc of the United Kingdom. Eastspring Investments companies (including JV’s) and Prudential plc are not affiliated in any manner with Prudential Financial, Inc., a company whose principal place of business is in the United States of America.














